Loss of critical business information and client privacy plus the threat of wider attacks and identity theft are among the far-reaching implications of an eavesdropping attack.
What does eavesdropping really mean?
Eavesdropping attack is the act of listening to, recording or intercepting private communications. It can apply to verbal conversations (phone calls or people talking face-to-face) and data communications (email, text messages, video conferences, fax transmissions, internet of things data streams or any other type of data that’s transmitted over a network).
Hackers can intercept communication between two devices, enabling easy access to private information. Devices like laptops and mobile phones with microphones can be remotely accessed and hacked, and an attacker can send data to anyone. Individuals or organizations can eavesdrop for various reasons such as cybercriminals trying to steal sensitive information and businesses trying to gain a competitive advantage. Attackers can eavesdrop on the conversation of apps that users often expect to be secured. They can also gain access to critical information to steal credentials or undertake identity thefts.
An eavesdropping attack, if undetected and not stopped early, can result in data and confidentiality security issues, the loss of crucial business information, and privacy. Sensitive company information, such as business secrets or user passwords, can be accessed and illegally exchanged. This can result in significant financial impact and damage the company’s reputation, too.
There are five main types of eavesdropping:
- Being close to people – attackers use audio or video gadgets to record sounds or images and turn them into electrical configurations for eavesdropping on the target.
- Interception of electronic communication – a transmission link or interface between two devices (sender and recipient) is tapped to eavesdrop.
- Image reconstruction – the display image of a PC can be reconstructed by using radio frequency emanations.
- Pertubation of the WiFi sytem – also referred to as data sniffing. It is used to target organizations and businesses whose communications within the network are sent to network ports. Hackers access the system and steal data.
- Pertubation of Digital Asset
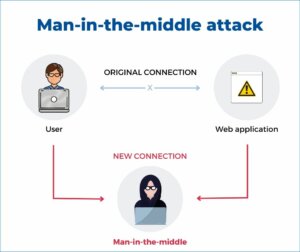
Passive vs. active eavesdropping – preventing the man-in-the-middle attack
Eavesdropping can be passive, where the attacker listens to digital conversations – for example VoIP or Voice over IP calls can be recorded and stored using protocol analyzers and converted audio files.
It can also be active. Hackers imitate websites where personal data and information is shared by online users – for example an MITM attack or man-in-the-middle attack. Data is captured, modified and sent to other devices without anyone noticing. Communication systems are hijacked and control over the transport of data is taken. Independent communications can be created with the users acting as if the conversation between users is private. MITM can also be referred to as lurkers in a social context. Lurkers gain knowledge by observing online. They rarely or never post. But like eavesdropping, lurking into other users’ private information is a privacy violation.
How can you keep your data safe?
Prevention is better than cure.
Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult, if not impossible, to detect and prevent passive network eavesdropping attacks. There are no tell-taledisruptions or changes to the network. Active attacks are easier to detect, but often, data is already intercepted by the time network changes are noticed.
Eavesdropping detection is difficult. That is why, with eavesdropping, prevention is better than cure. It is why it is important to maximize cyber security effectiveness.
For best protection you could firstly:
- Consider what data you should store on your device as attackers can use sophisticated hacking apps to access your mobile stored information.
- Be cautious when installing applications – research them and check what permissions are required. Malicious apps are often disguised to look like an attractive package but carry Trojan horse virus code.
- Avoid connections to unknown WiFi networks, and not using public WiFi networks. Fake WiFi hotspots can be created to hack mobile phones.
- Enable encryption on your WiFi network.
Secondly, choose a solution such as WAVETRAP from WAVE by AGC. The transparent glass product from WAVE by AGC can help support best cyber security practices by serving as a physical barrier that prevents digital eavesdropping while also ensuring compatibility with sensitive and even critical electronic systems. A physical firewall can be added as an additional and tailored layer of protection against commonplace threats and multi-stage attacks. It can ward off unwanted visitors.
With WAVETRAP, operations can introduce best practices, elevate their protection against eavesdropping, and be confident in the increased safety and security of their communications.
Here are some other articles that might be of interest to you:
Why it might be time for a digital deter
Are you protected against eavesdropping attacks?

