Introduction about the mobile network
In order to distribute the mobile signal the operators place a series of base stations on the territory. These antennas emit signals for 2G/3G/4G/5G technologies in several frequency bands ranging from 800MHz to 6GHz. The mobile phone antennas are distributed evenly over the territory to ensure a homogeneous coverage.
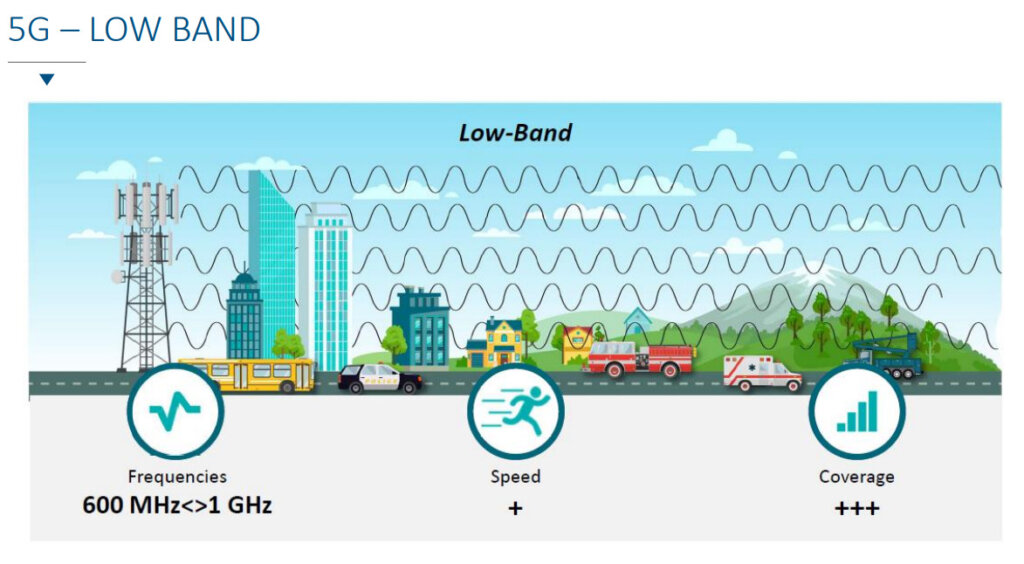
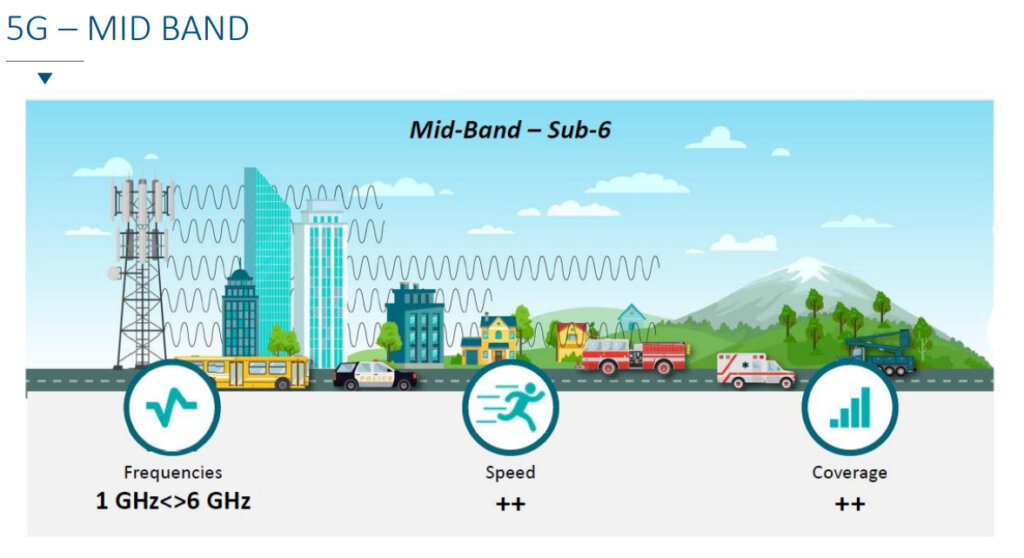
Operators use low frequency bands and high frequency bands to distribute the signal. The low bands are used to cover the territory, they propagate better and further but the associated quality of service is low and the number of users that can be addressed is lower, the high bands as for it propagate less well but give a better quality of service and allow to address more users. In terms of signal propagation, the signal from the base stations propagates like sound, the further away from the source the lower the signal. The higher the frequency the stronger and faster the attenuation.
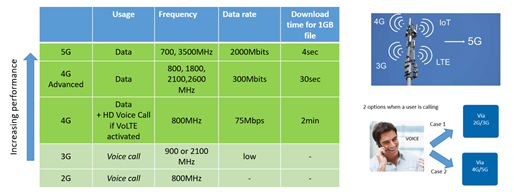
source : https://ir.kontron.ag/5G_in_Iot__Update_on_AI_Neumann.pdf
Operators size their network to have an acceptable signal strength outside and inside buildings. Operators combine low frequency and high frequency approaches to provide mobile coverage that can address enough users outdoors and indoors. In their design a reasonable attenuation of about 10dB is taken into account for buildings.
At the technology level, several technologies coexist at the same time.
Impact of envelope attenuation
Mobile equipment requires two important elements : signal strength and signal quality. Below a certain threshold, the mobile equipment does not detect any signal and does not work anymore.

Coverage problems can occur for recent buildings that strongly attenuate mobile waves (attenuation < 30dB). In this case the building is out of the assumptions of attenuation used to size the networks used by operators and problems may appear.
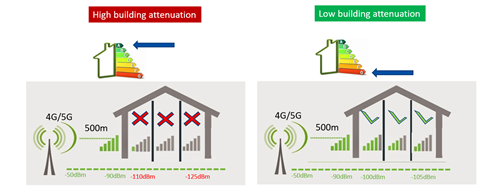
In this type of building the outdoor signal is good, but inside the signal is weak and at the limit of sensitivity of phones and often available only in low band. This translates for the end user into :
- NO signal available or only very close to the windows, once the user moves inside the building the signal fades and the phone cuts out
- – A signal only available in the low band, i.e. a frequency used for coverage that can serve a limited number of users. During peak hours these bands can be saturated and the service can stop.
- A signal available only in old technologies (2G/3G) that offer a very limited service (low quality apple)
Why do my calls stop?
A call can stop for several reasons
- either the signal level goes below the sensitivity threshold of the phone, this can happen for example in buildings that are highly hermetic to mobile waves
- or because the network is saturated and there are too many users, for example if my mobile phone is on a low band during the rush hour periods typically these bands are more quickly congested and the network can eject the users with a weak signal in order to force them to connect on another station and free capacities for the others
- or because the phone is constantly changing technology because no signal is dominant and strong enough within the building.
Why can’t the person I’m talking to hear me or why does the communication stop in the middle?
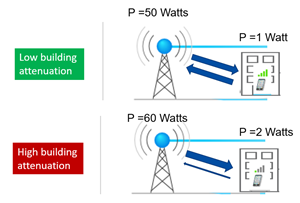
Communication systems work in two directions, there is a downlink and an uplink. For a communication to be established, both links must be established in a reliable way. On the other hand, mobile systems constantly adapt their power according to the quality of the communication channel, whether it is at the base station or the GSM. The base station is more powerful than the mobile. The mobile is limited in power for health reasons.
In buildings with high attenuation, the uplink from the mobile will be the first to be degraded because of the limited power of the phone. In this type of building the signal from the base station is able to get in but the cell phone is not able to send its signal to the base station even though it is transmitting at full power. As a result, the end user can hear the caller but cannot answer.
What is a Faraday cage?
A Faraday cage is a metal enclosure that prevents certain electromagnetic radiation from entering or leaving the enclosure. The cage was invented in the 19th century and has a variety of applications in everyday life to protect sensitive electronic equipment or people. For example, Faraday cages are used in medical settings to prevent radio signals from entering the room and interfering with equipment, or in kitchen microwaves to trap microwaves inside the machine so they heat your food and don’t escape.
A Faraday cage is made of any electrically conductive material. This cage can be made of wire mesh, metal sheets or wire coils. It can be any shape, such as a box, sphere or cylinder, and any size, from extremely small to extremely large. Faraday cages can be quite complex or very simple, ranging from a shoebox to an entire building.

source : https://www.comsol.com/blogs/faraday-cages-say-do-not-pass-to-electromagnetic-waves/
In the building sector, recent buildings behave more and more like a Faraday cage, i.e. they strongly attenuate the mobile waves present outside.
This phenomenon is due to the fact that the materials used to build the facades, i.e. walls, insulation, glazing, contain more and more metallic elements. The walls contain metal reinforcements, the insulating panels are made with PU deposited on layers of aluminum and the glazing contain metal layers.
Concerning glazing, it is interesting to note that currently all glazing on the market contain one or more invisible metallic layers in order to obtain high thermal performance. These layers allow to keep the heat and avoid overheating in the building. All these metallic coatings stop mobile waves.
What is a good mobile connectivity in the end?
A good mobile connectivity is a signal strong enough to be above the sensitivity thresholds and a network sized to serve all users.
Get in touch with us to evaluate your building connectivity and improve the phone calls quality of its occupants thanks to our WAVE by AGC solutions.

